The Real Reason You Can't Stop Eating Junk Food
In a world brimming with fast food and snacks, resisting the lure of junk food is a daily struggle for many. But what makes junk food so addictive? This article delves into the science behind our cravings, revealing why we can't seem to get enough of those sugary, salty, and fatty treats.
The Role of Food Addiction
Food addiction plays a significant role in our inability to resist junk food. It operates similarly to drug addiction, engaging the same areas of the brain. Highly palatable foods, often packed with sugar, fat, and salt, trigger the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This dopamine release creates a sense of euphoria, encouraging repeated consumption despite negative health consequences. The powerful impact on the brain's reward system explains why junk food can lead to compulsive eating patterns akin to drug addiction.
The Extraordinary Science of Junk Food
Food manufacturers are critical in perpetuating junk food addiction. They employ extensive research and sophisticated technology to create the perfect combination of sugar, fat, and salt that maximizes the pleasure response in our brains. This process, known as the "bliss point," is meticulously engineered to make products irresistible. By continuously testing and refining their recipes, food manufacturers ensure their products trigger the strongest possible cravings, leading consumers to overeat. This deliberate manipulation of our taste preferences is a key factor in the widespread addiction to junk food and the resulting health consequences. The strategic efforts by food manufacturers to enhance the addictiveness of their products highlight the need for greater awareness and regulation to protect public health.
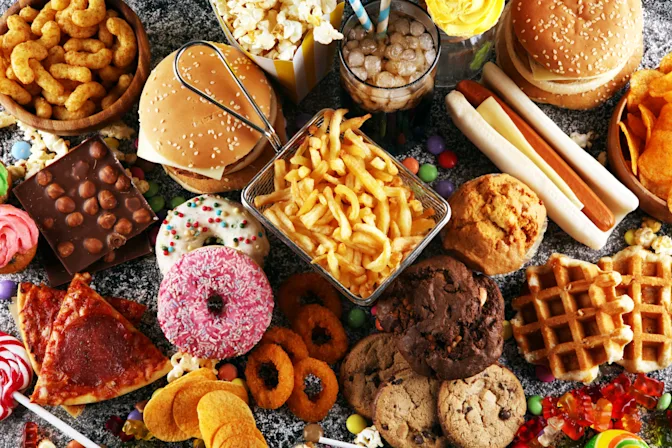

The Obesity Epidemic
The addictive nature of junk food significantly impacts the global obesity epidemic. The widespread availability and aggressive marketing of highly processed foods contribute to increasing obesity rates worldwide. Today, 42% of U.S. adults and about 20% of children and adolescents aged 2 to 19 years are considered clinically obese. As people consume more junk food, their bodies become conditioned to crave these high-calorie, low-nutrient options, leading to excessive calorie intake and weight gain. This cycle of addiction not only affects individual health but also places a substantial burden on healthcare systems, as obesity is linked to numerous chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension.
The Power of Marketing
Marketing plays a crucial role in widespread addiction to junk food. Food manufacturers invest heavily in advertising campaigns that appeal to emotions and sensory experiences, often targeting vulnerable populations such as children and young adults. These companies use vibrant packaging, catchy slogans, and strategic product placements to make junk food appear more desirable and essential in daily life. By creating an environment where highly processed foods are constantly advertised and readily available, these marketing tactics normalize the consumption of unhealthy products, further entrenching addiction and contributing to the obesity epidemic. Recognizing and regulating these manipulative marketing strategies is essential in the fight against junk food addiction and its associated health risks.

Breaking the Cycle of Addiction
Understanding the science behind junk food addiction is the first step toward managing it. Practical strategies to break free from this cycle include mindful eating, planning meals, and choosing whole, unprocessed foods. Additionally, becoming aware of the tactics used by food manufacturers can help consumers make more informed choices. By recognizing the mechanisms at play, we can all take steps to improve our eating habits and prioritize our health.
References: How to Identify and Manage Food Addiction | The Extraordinary Science of Addictive Junk Food | The Science Behind Junk Food Addiction