8 Brain Boosting Benefits of Swimming
Swimming is more than just a full-body workout; it also offers a wealth of benefits for your brain. Here are eight reasons why you should consider adding swimming to your routine for enhanced brain health.
1. Enhances Memory and Cognitive Function

Swimming has been shown to improve memory and cognitive function. The exercise increases levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that boosts neural plasticity. This enhances learning, memory, and cognitive performance. Studies have found a strong relationship between BDNF levels and the size of the hippocampus, the brain region responsible for these functions.
2. Reduces Stress and Improves Mood

Swimming triggers the release of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which reduces depression and anxiety while improving mood. The endorphins released during swimming bring about a sense of euphoria, making it an excellent way to relieve stress.
3. Promotes Neurogenesis

Regular aerobic exercise, including swimming, contributes to neurogenesis, the process of creating new neurons. This helps repair brain damage and maintain overall brain health. Research shows that swimming can enhance the development of dendritic spines, which are essential for neuron connectivity.
4. Increases Blood Flow to the Brain

Swimming increases overall brain blood flow more effectively than land-based exercises. Water immersion, combined with the horizontal position in swimming, facilitates better blood circulation to the brain, ensuring it receives more oxygen and nutrients.
5. Reduces Artery Stiffness

Swimming is highly effective in reducing artery stiffness, a common issue that can lead to brain and kidney damage. According to BBC, a study by Prof. Hiro Tanaka from the University of Texas showed that a three-month swimming program significantly reduced arterial stiffness, thereby reducing stress on the brain.
6. Supports Neuron Survival and Reduces Cognitive Decline
Studies in rats have shown that swimming can stimulate brain pathways that suppress inflammation and inhibit apoptosis (cell death) in the hippocampus. These benefits support neuron survival and reduce cognitive decline associated with aging.
7. Enhances Short- and Long-Term Memory
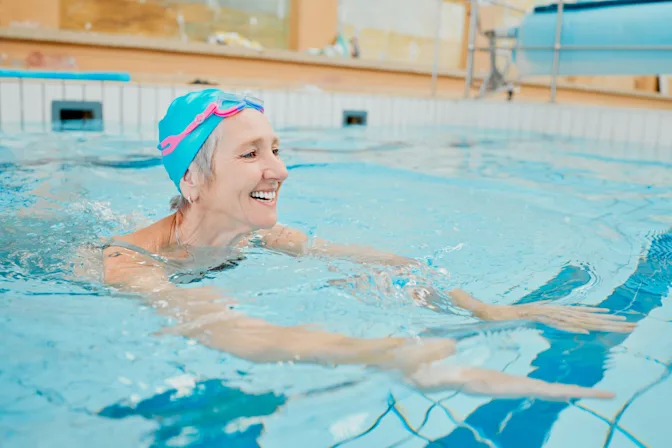
Research involving rats demonstrated that just seven days of swim training improved both short- and long-term memory. This suggests that swimming could be used to repair learning and memory damage caused by neuropsychiatric diseases in humans. Similar studies in humans have shown improved mental acuity in elderly swimmers.
8. Boosts Cognitive Function in Children

Swimming also benefits young, developing brains. Research has shown that children who swim have better accuracy in recognizing new vocabulary words compared to those who engage in other physical activities. This highlights the cognitive benefits of swimming for children's learning and development.
Swimming offers a unique combination of physical and mental health benefits. From enhancing memory and cognitive function to reducing stress and promoting neurogenesis, the advantages of regular swimming extend far beyond the pool. Whether you are young or old, adding swimming to your exercise routine can provide significant boosts to your brain health. So, take the plunge and experience the holistic benefits of swimming for your mind and body.
References: Why swimming could be the best exercise you do | The fountain of youth hasn't been found — but swimming may come close