6 Essential Tips for Avoiding Salmonella
Salmonella is a common cause of food poisoning, making it essential to know how to protect yourself and your loved ones from this infection. Let's explore six simple tips to help you avoid and prevent salmonella.
What Is Salmonella?
Salmonella is a type of bacteria that can cause illness in humans commonly found in a variety of foods, including raw meat, poultry, eggs, and unwashed fruits and vegetables. Contaminated foods often look and smell normal, making it challenging to detect without proper precautions.

1. Always Wash Your Hands
One of the most effective ways to prevent Salmonella infection is by practicing good hand hygiene. Always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and running water after using the bathroom, changing diapers, and before handling or eating any food.
It is equally important for persons with diarrhea, especially children, to wash their hands carefully and frequently to reduce the risk of spreading the infection. Additionally, wash your hands after contact with animals, animal feces, and animal environments.
2. Handle Food With Care
Proper food handling is crucial in preventing Salmonella infection. Keep raw meat and poultry separate from produce and other foods when shopping and storing groceries.
After handling uncooked poultry, wash your hands, cutting boards, countertops, cutlery, and utensils. Make sure to wash raw fruits and vegetables before eating. Be mindful that food and kitchen tools and surfaces may become contaminated from raw food products, so use separate cutting boards for raw meat and vegetables to avoid cross-contamination.
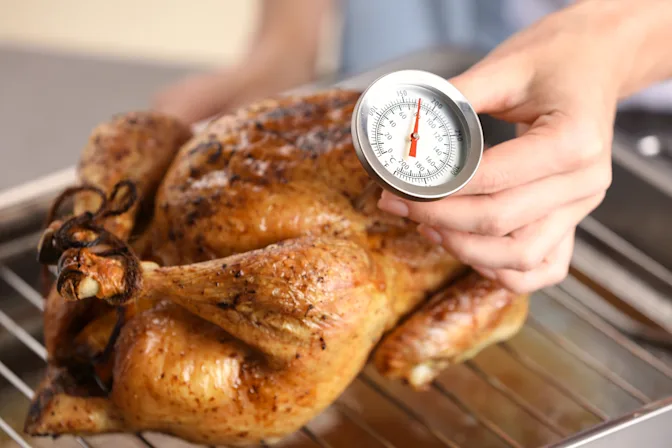

3. Cook and Store Food Safely
Cooking and storing food at the correct temperatures can help destroy Salmonella bacteria. Do not eat raw or undercooked eggs and use pasteurized eggs for dishes that do not require cooking, such as hollandaise sauce or homemade ice cream.
Thoroughly cook raw meat, poultry, and hamburgers until they are no longer pink in the middle. When it comes to proper storage, defrost food in the refrigerator, in cold water, or in the microwave. Store food in a refrigerator that is 40°F or cooler or a freezer that is 0°F or cooler. Unpasteurized milk and foods made from unpasteurized milk can be sources of Salmonella, so always opt for pasteurized products.
4. Be Cautious Around Animals
Salmonella can spread from animals to humans, so it is important to handle pets and other animals safely. After touching pets, their food, water, waste, or belongings, wash your hands thoroughly with warm running water and soap.
Avoid putting your hands in your mouth after petting or playing with animals, and do not kiss pets or animals. Keep high-risk individuals, such as children under five and people with weakened immune systems, away from high-risk animals like turtles, frogs, chickens, or ducks.
Cleaning your pet's habitat and belongings outdoors if possible. If you must clean indoors, use a bathtub or large sink that can be disinfected afterward.

5. Swim Safely to Avoid Infection
Salmonella can also be contracted through contaminated water, so use caution when swimming. Avoid swallowing lake or pool water.
Anyone with a diarrheal illness should also avoid swimming in public pools or lakes, sharing baths, and preparing food for others.
6. Stay Vigilant During Summer
Salmonella is more common in the summer due to warmer weather and unrefrigerated foods providing ideal conditions for the bacteria to grow. Be vigilant about refrigerating or freezing perishables, prepared foods, and leftovers within two hours, or within one hour if the temperature is 90°F or hotter.
By taking simple precautions such as proper hand washing, careful food handling, and avoiding contact with high-risk animals, you can greatly reduce your risk of contracting Salmonella. Stay informed, practice these safety tips, and enjoy a healthier life free from foodborne illnesses.
References: Prevention | General Information | Salmonella | Preventing Salmonellosis